Episode 0x0F: Argo Events
Table of Contents
NOTE: Many commands in this post make use of specific constants tied to my own setup. Make sure to tailor these to your own needs. These examples should serve as a guide, not as direct instructions to copy and paste.
NOTE: Check out the final code at geekembly and homelab repositories on my Github account.
Introduction
In the previous episode, we discussed the individual components necessary to create a weblog using Hugo, alongside implementing a CI/CD pipeline. In this episode, we will integrate these components using Argo Events. Specifically, we will set up an EventSource to receive webhooks from GitHub, and a Sensor to trigger our CI/CD pipeline in response to push events.
Installation
We can install Argo Events similar to our previous applications. Add the following to your apps.yaml file:
- apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: argo-events
namespace: argocd
spec:
destination:
namespace: argo-events
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
project: default
source:
chart: argo-events
repoURL: https://argoproj.github.io/argo-helm
targetRevision: 2.4.6
helm:
releaseName: argo-events
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
Then apply the configuration:
kubectl apply -f apps.yaml
Geekembly Deployment
With Argo Events installed, we need to modify our weblog deployments to leverage it.
Event Bus
First, create an event bus by adding this to an events.yaml file:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: EventBus
metadata:
namespace: geekembly
name: default
spec:
nats:
native:
replicas: 3
auth: token
Event Source
Provide your GitHub Personal API token created in episode 11 by running:
kubectl create secret generic github-access -n <namespace> --from-literal=token=<github-token> --from-literal=secret=<webhook-secret> --dry-run=client -o yaml | kubeseal -o yaml
Add an event source to handle GitHub webhooks to events.yaml:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: EventSource
metadata:
namespace: geekembly
name: github
spec:
eventBusName: default
service:
ports:
- port: 12000
targetPort: 12000
github:
geekembly:
repositories:
- owner: cih2001
names:
- geekembly
webhook:
endpoint: /push
port: "12000"
method: POST
url: https://github.<your-domain>.com
events:
- "*"
apiToken:
name: github-access
key: token
webhookSecret:
name: github-access
key: secret
insecure: false
active: true
contentType: json
Argo Events will automatically configure the GitHub webhook on our project to receive events on https://github.<your-domain>.com. Also configure your ingress to route events to this event source:
- host: github.geekembly.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: github-eventsource-svc
port:
number: 12000
Sensor
In the CI step, we will check for changes in the blog contents. If any changes are detected, we’ll create a new Docker image and tag it. This tag will then be passed to our CD pipeline, where the deployment tag in our Kustomize file will be updated accordingly. The updated Kustomize file will be committed back to the main branch, which will subsequently trigger Argo CD to synchronize the deployment automatically.
Sensors in Argo Events listen to specific events and trigger actions based on those events. Create a sensor to respond to GitHub push events and trigger your CI/CD pipeline by creating a sensor.yaml file:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Sensor
metadata:
name: github
namespace: geekembly
spec:
template:
serviceAccountName: default
dependencies:
- name: github-dep
eventSourceName: github
eventName: geekembly
filters:
data:
- path: headers.X-Github-Event
type: string
value:
- push
triggers:
- retryStrategy:
steps: 3
template:
name: github-workflow-trigger
k8s:
operation: create
source:
resource:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: prod-ci-workflow-
namespace: geekembly
spec:
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: workspace
spec:
accessModes: ["ReadWriteOnce"]
resources:
requests:
storage: 200Mi
volumes:
- name: ssh-vol
secret:
secretName: github-ssh-key
- name: docker-vol
secret:
secretName: regcred
entrypoint: main
templates:
- name: main
steps:
- - name: ci-step
templateRef:
name: prod-ci
template: start
- - name: cd-step
templateRef:
name: prod-cd
template: start
arguments:
parameters:
- name: push-skipped
value: "{{steps.ci-step.outputs.parameters.push-skipped}}"
- name: release-tag
value: "{{steps.ci-step.outputs.parameters.release-tag}}"
Perhaps you also want to add more filters or configuration to the event triggers and actions. Refer to the Argo Events documentation for additional customization.
NOTE: prod-ci and prod-cd are workflow templates we created based on smaller components we discussed in the episode 14. Please checkout the full source code at geekembly.
Testing Pipeline
The above setup should activate a fully operational CI/CD pipeline. To test it, push changes to the main branch and verify that the pipeline is triggered.
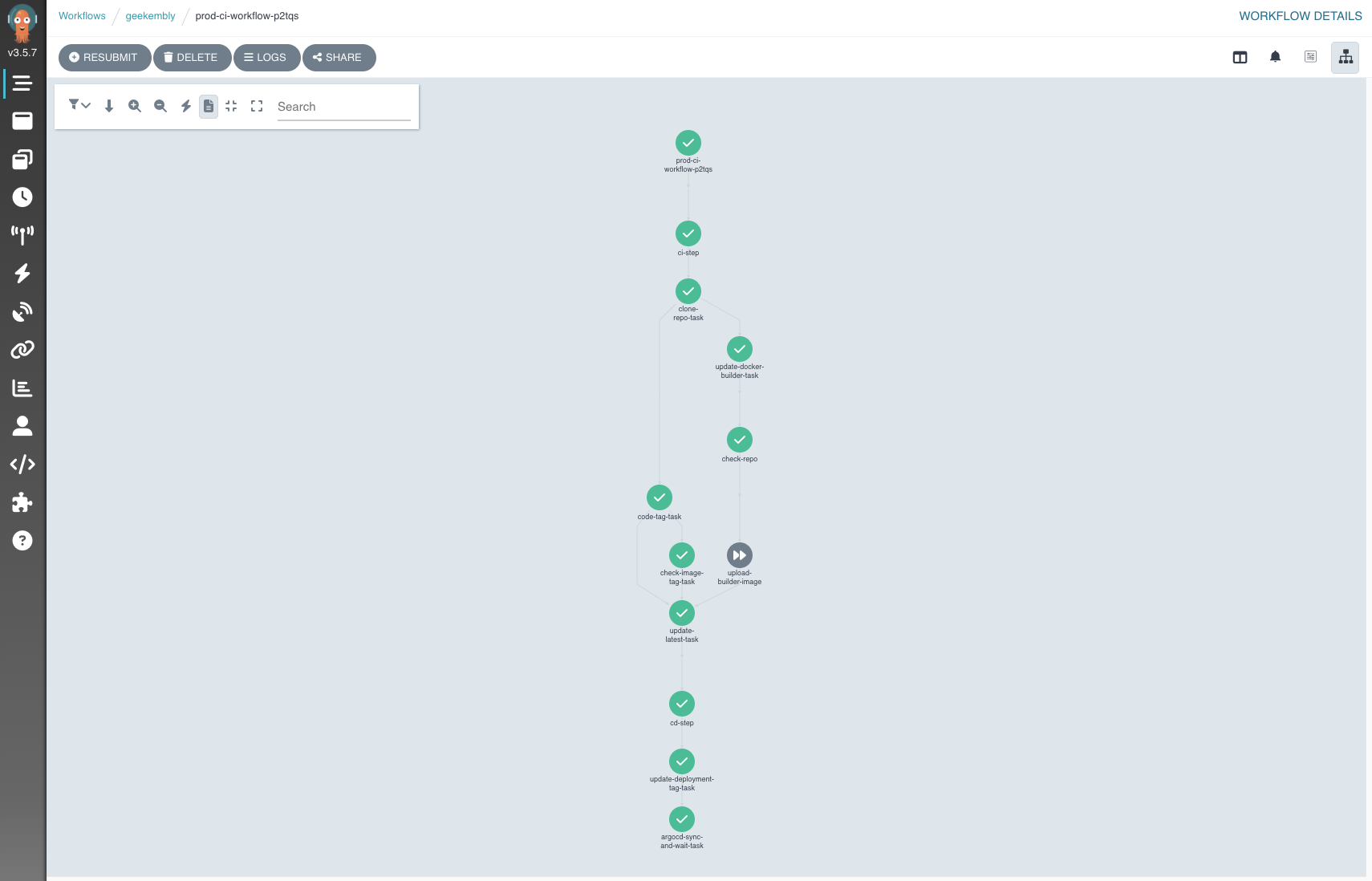 .
.
To view pipeline logs, use:
argo logs -n geekembly @latest --follow
Conclusion
Many different designs can be adopted to structure a CI/CD pipeline. The approach described here is just one example. Explore and experiment to suit your specific needs. You may want to enhance your pipeline to include setting up multiple environments, such as staging or per-PR environments.
In the next episode, we will integrate Prometheus and Grafana to monitor visits, downtimes, and the overall health of our Kubernetes cluster. Stay tuned! 🚀