Episode 0x10: Prometheus, Alert Manager and Grafana
Table of Contents
NOTE: Many commands in this post make use of specific constants tied to my own setup. Make sure to tailor these to your own needs. These examples should serve as a guide, not as direct instructions to copy and paste.
NOTE: Check out the final code at homelab repositories on my Github account.
Introduction
Having a functioning weblog is one thing; gaining insights from it is another. Leveraging Prometheus for metrics collection and Grafana for visualization, we can create an insightful dashboard for our weblog.
Installation
We’ll install the Prometheus stack using its community Helm charts via an Argo CD application. First, add the following application configuration to your apps.yaml file:
- apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: kube-prometheus-stack
namespace: argocd
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts
chart: kube-prometheus-stack
targetRevision: 60.3.0
helm:
releaseName: kube-prometheus-stack
values: |
namespaceOverride: monitoring
grafana:
ingress:
enabled: true
ingressClassName: nginx
annotations:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: "letsencrypt-prod"
acme.cert-manager.io/http01-edit-in-place: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"
hosts:
- grafana.<your-domain>.com
tls:
- hosts:
- grafana.<your-domain>.com
secretName: grafana.<your-domain>.com-tls
path: /
destination:
namespace: monitoring
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
syncPolicy:
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
- ServerSideApply=true
This configuration will install the Prometheus stack in the monitoring namespace. It also sets up the Grafana ingress, allowing us to access Grafana later on. For Prometheus, no ingress configuration is needed; its web UI can be accessed via port-forwarding.
Apply this configuration with:
kubectl apply -f apps.yaml
Next, change the Grafana admin password:
argocd app set kube-prometheus-stack -p 'garafana.adminPassword=<grafana-admin-password-here>'
Test Prometheus
To verify Prometheus, port-forward from your machine to the Prometheus service:
kubectl port-forward -n monitoring svc/kube-prometheus-stack-prometheus 9090:9090
Visit https://localhost:9090 in your browser. Navigate to Status > Targets to view the configured targets, which should be already set up.
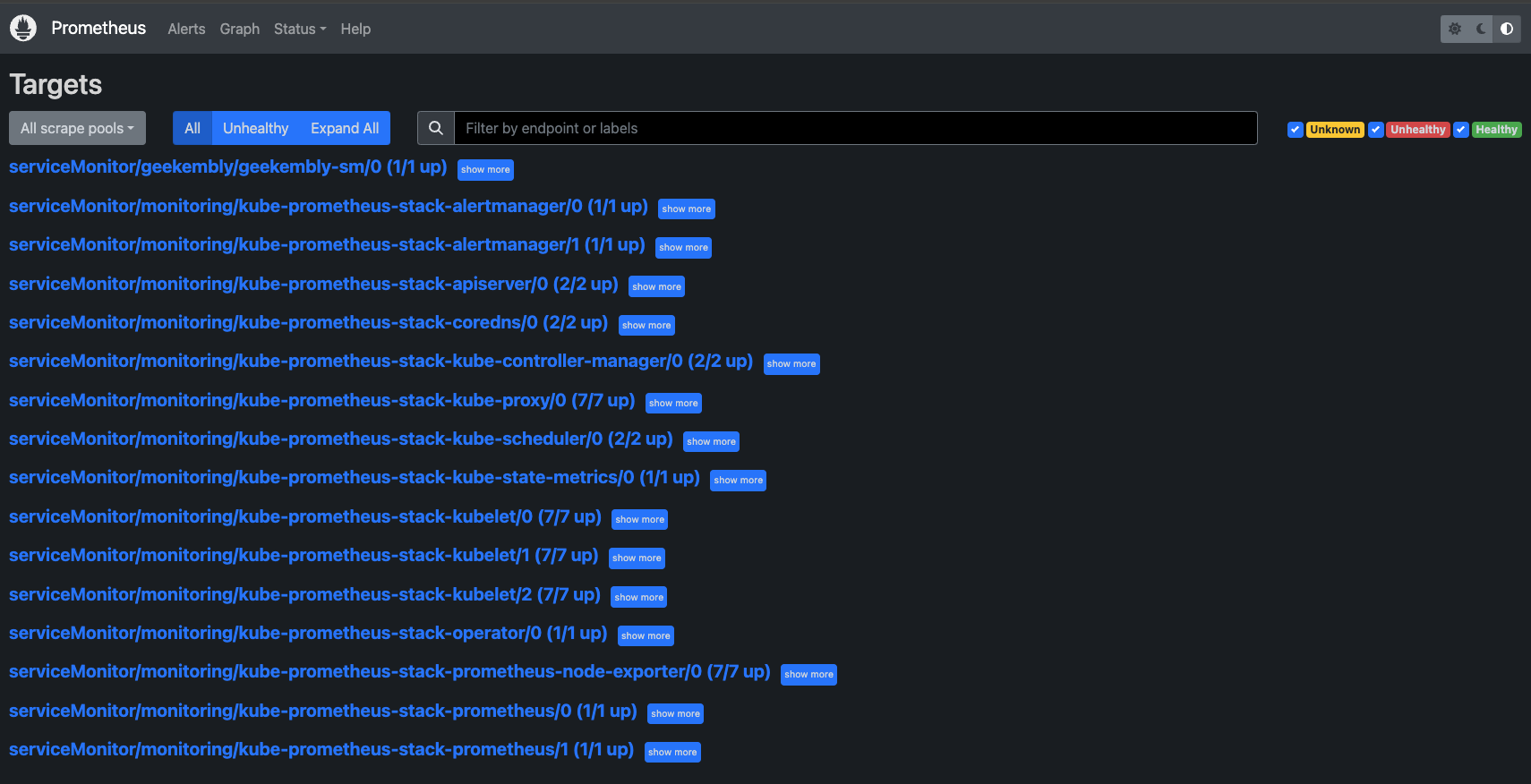
If the kube-proxy target does not appear healthy, modify its configuration to bind metrics on all interfaces:
kubectl edit cm -n kube-system kube-proxy
Change metricsBindAddress: 127.0.0.1:10249 to metricsBindAddress: 0.0.0.0:10249.
Test Grafana
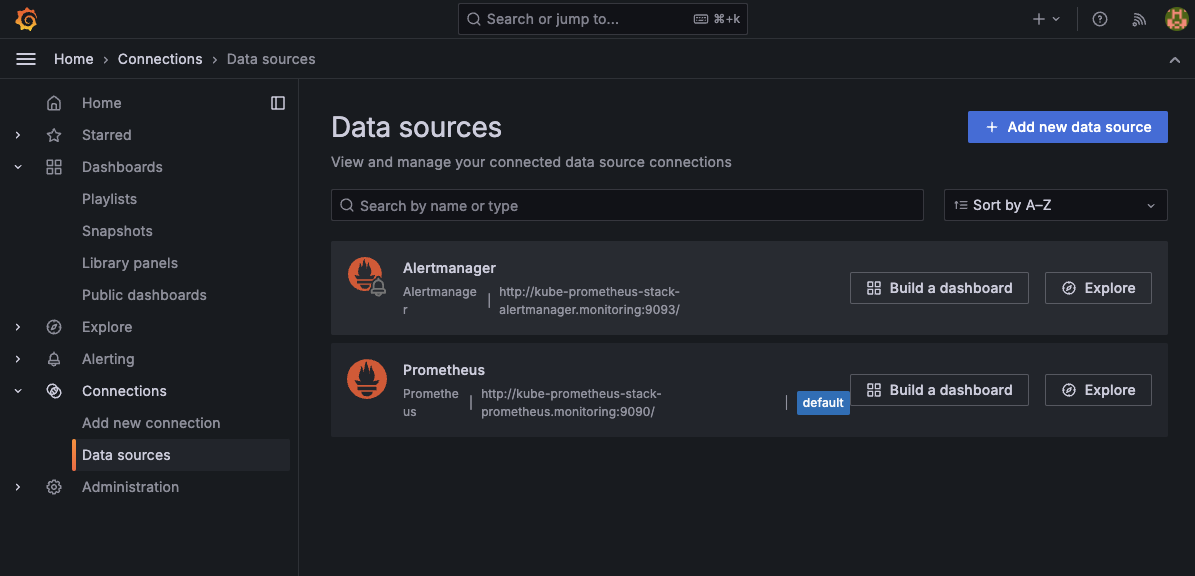
Open your browser and navigate to https://grafana.<your-domain>.com. Log in using your admin credentials. You should see Alertmanager and Prometheus already listed as data sources.
Additionally, some default dashboards should be pre-configured.
Geekembly Metrics
Prometheus Nginx Exporter
To gain insights from our weblog, Geekembly, we’ll configure an Nginx Prometheus exporter to expose Nginx metrics.
Add the Nginx exporter as a sidecar to your current deployment by modifying your deployment.yaml as follows:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: geekembly-dpl
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: geekembly
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: geekembly
spec:
containers:
- name: geekembly
image: geekembly:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: http
volumeMounts:
- name: nginx-config
mountPath: /etc/nginx/conf.d/nginx_status.conf
subPath: nginx_status.conf
- name: nginx-exporter
image: nginx/nginx-prometheus-exporter:latest
args:
- -nginx.scrape-uri=http://localhost:8080/stub_status
ports:
- containerPort: 9113
name: metrics
volumes:
- name: nginx-config
configMap:
name: nginx-config
imagePullSecrets:
- name: regcred
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
namespace: geekembly
name: nginx-config
data:
nginx_status.conf: |
server {
listen 8080;
location /stub_status {
stub_status;
allow all;
}
}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: geekembly-svc
labels:
app: geekembly
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
name: http
protocol: TCP
- port: 9113
name: metrics
protocol: TCP
selector:
app: geekembly
The Nginx exporter exposes metrics on port 9113 for Prometheus to scrape, while Nginx exports stub_status on port 8080.
Next, configure Prometheus to scrape this new endpoint using a custom resource definition (CRD) called ServiceMonitor. Create a servicemonitor.yaml file with the following content:
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: ServiceMonitor
metadata:
labels:
release: kube-prometheus-stack
name: geekembly-sm
namespace: geekembly
spec:
endpoints:
- port: metrics
interval: 30s
selector:
matchLabels:
app: geekembly
Apply all these configurations, then navigate to the Prometheus targets page to verify the new target for your weblog is active.
Grafana Dashboard
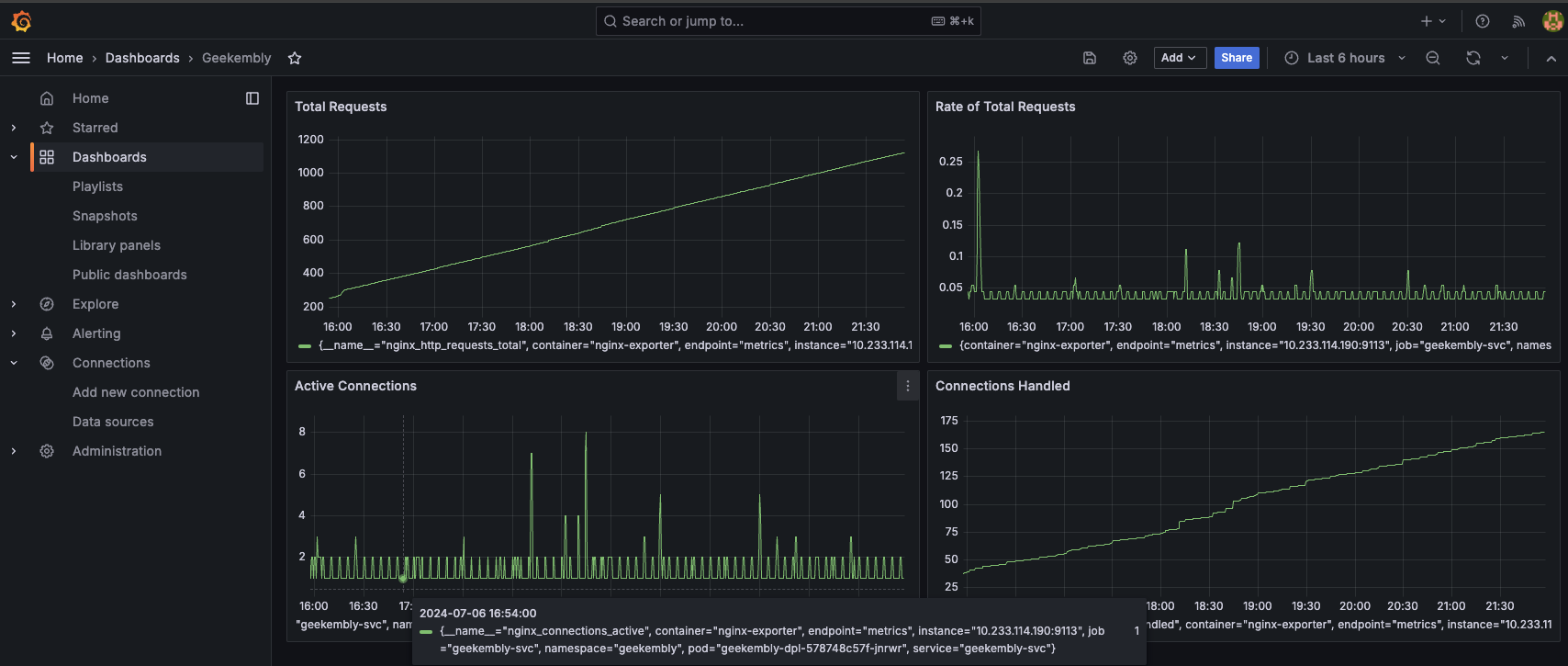
Now that Prometheus collects Nginx metrics, we can create a Grafana dashboard to visualize them.
- Navigate to
Grafana > Dashboards > New Dashboard > Add Visualization. - Select Prometheus as the data source.
- Add
nginx_http_requests_totalas a metric and set the title toTotal Requests. - Save the dashboard.
Similarly, you can add visualizations for total HTTP requests rate, active connections, and connections handled.
Conclusion
We’ve successfully set up a comprehensive monitoring solution using Prometheus for metrics collection and Grafana for visualization. This setup allows us to gather and analyze data from our weblog and the cluster in which it runs. In the next episode, we’ll integrate Grafana Loki and Alloys for log collection and visualization. Stay tuned! 🚀